For wideband transponders that transmit several narrowband carriers, or one or few wideband carriers, the concept of time slicing — as defined in the DVB-S2 standard (EN 302 307-1 Annex M) — allows the receivers to pre-select specified streams already in the physical layer (PL) carrying one or more services. The DVB-S2x standard (EN 302 307-2 Annex E) also specifies a format for time slicing.
For broadcast interactive or professional applications (e.g., IPTV services, direct-to-home (DTH) offerings, occasional use (OU), etc.), which can use a wideband carrier to allow efficient transponder usage, time slicing permits the operation of demodulators with high-speed input processing and standard FEC and output processing.
The conventional DVB-S2 multistream operation also uses multiplexing techniques in the baseband frame layer, but the header of the underlying physical layer only carries information about modulation, coding parameters, and the presence of pilots.
Once the FEC processing is over, the receiver can discard unused data. In time-slicing mode, the PL header contains additional stream-specific information, which supports certain portions of the multiplex at the physical layer processing within the receiver.
Only required information is forwarded to the FEC and output processing. With time slicing, a cost-effective receiver can be realized for wideband applications.
For time slicing, address information can be found in an extension of the PL header of each physical layer frame.
This address information is called time-slicing number (TSN) or time-slicing indicator (TSI), whereby the TSN/TSI can have the same value as the input stream identifier (ISI) in the MATYPE-2 field of the baseband header.
Therefore, each time slice of the wideband carrier can be identified by TSN/TSI. These time slices are suitably spaced in time and correspond to one PL frame. (See Figure 1.)
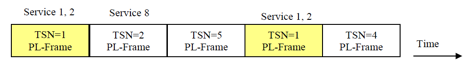
Figure 1. Typical sequence of PL frames
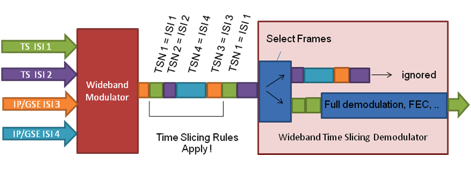
Figure 2. Typical time-slicing application
Ggf: obsolete:
Through the TSN in the PL frame, the receiver can early on detect specific streams, which shall be received and decoded by the FEC decoder of the receiver, while the other streams with unknown address information of the wideband carrier are discarded.
As a result, receivers still have to provide high-speed demodulation, particularly in the PL header processing and tracking, but may process the FEC with significant lower speed than that of the wideband carrier.
On the transmitting side, time-slicing algorithms can be adapted to specific applications in order to provide optimal efficiency and flexibility.
The wideband symbol rate can be sliced constantly into “virtual carriers” of equal or different capacity for broadcast use cases as well as dynamically following traffic requirements for ACM applications. (See Figure 2.)


